In general, the nonlinear behavior is due to the dependence of the polarization P(t) on
the applied electric field, E(t). Assuming an isotropic dispersive material, Maxwell’s
equations are:
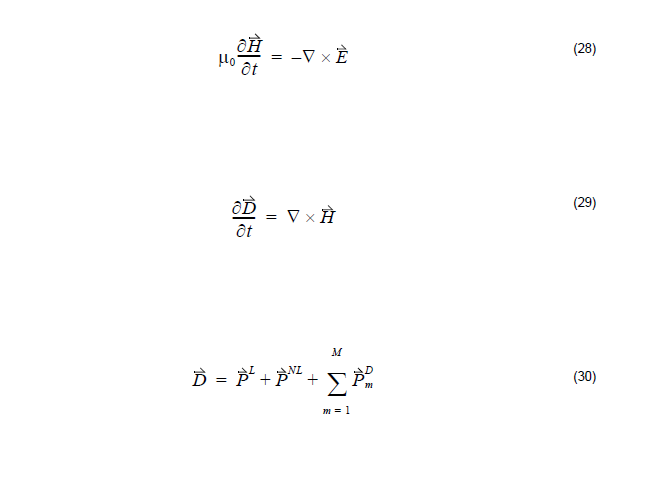
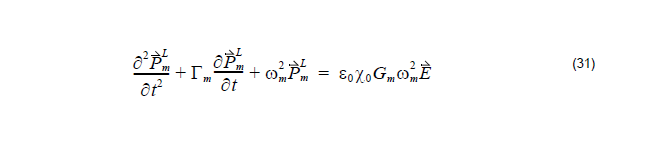
where PL represents the linear polarization, in general ![]() is the dispersive polarization which is controlled by Lorentz model in Equation 20 and
is the dispersive polarization which is controlled by Lorentz model in Equation 20 and
denotes the nonlinear polarization.
The nonlinear polarization ![]() may come from various model sources that produce the different nonlinear phenomenon. Currently OptiFDTD can handle four kinds of nonlinearity:
may come from various model sources that produce the different nonlinear phenomenon. Currently OptiFDTD can handle four kinds of nonlinearity:
- Dispersive second-order nonlinear material
- Dispersive third-order nonlinear material
- Dispersive Kerr effect
- Dispersive Raman effect

