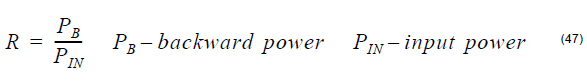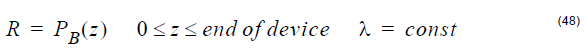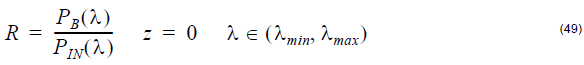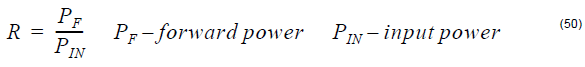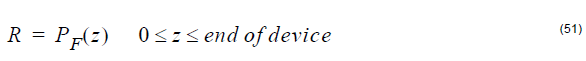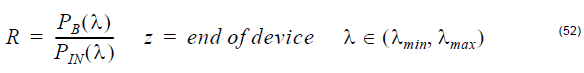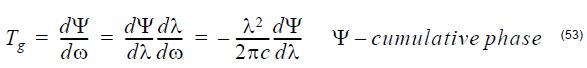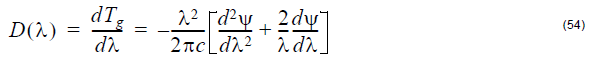Reflection
Reflection at a given position is defined by the ratio of back-reflected power to input
power:
The program calculates reflection for both coupled modes, called Reflection 1 and
Reflection 2 respectively.
- For Propagation calculations, the reflection is obtained at every point along the
grating device. In the case of multiple gratings, the device begins with the first
grating and ends with the last grating:
- For Spectrum calculations, the reflection is obtained at the end of the device
Transmission
Transmission at a given position is quantified by the ratio of forward-carried power to
input power:
The program calculates transmission for both coupled modes, called Transmission 1
and Transmission 2 respectively.
- For propagation calculations, the transmission is obtained at every point along
the grating device. In the case of multiple gratings, the device begins with the first
grating and ends with the last grating:
- For spectrum calculations, the transmission is obtained at the end of the device.
Cumulative Phase
Cumulative Phase is the phase change of the electromagnetic field accumulated for
a given wavelength.
Group Delay
Group Delay is the first derivative of the cumulative phase with respect to the angular
frequency.
Dispersion
Dispersion is defined as the first derivative of the group delay with respect to the
wavelength.