Effective Nonlinear Refractive Index
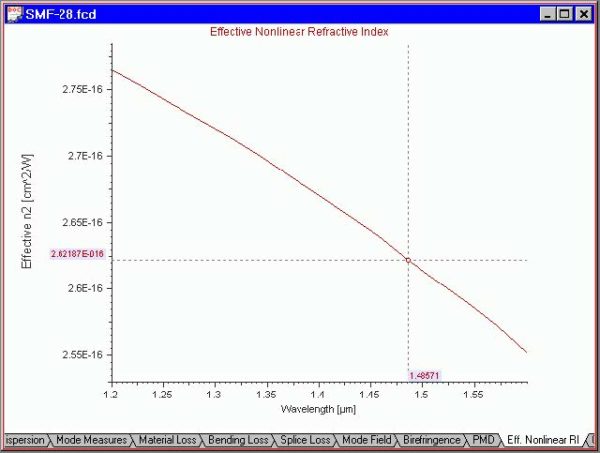
This view shows you the eff. nonlinear refr. index of the fiber as determined by the nonlinearity of the bulk materials and the degree of confinement. To access this view do one of the following steps: Step Action 1 Select the “Eff. Nonlinear RI” tab in the “Views” window 2 Select “Views/Effective Nonlinear Refr. Index”…
Script Language
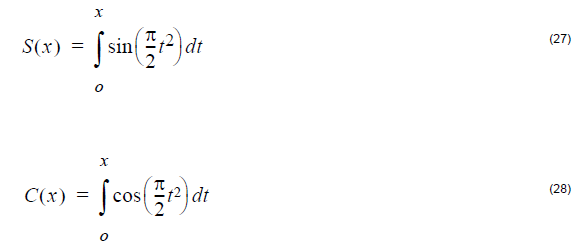
Overview of Script Language The script language OptiFiber uses is a programming language based on the BASIC language syntax. You use the script language to define the fiber profile, or material dispersion, for example. To start programming with the Script Language, you have to choose the User Defined option in OptiFiber dialog boxes. The script…
Fiber Mode Solvers
Introduction Many kinds of optical fiber can be described, or in the case of graded index fibers, approximated by, a series of concentric layers of loss-less dielectric. When the index contrast in the structure is small, it is common to use the scalar wave equation to obtain the linearly-polarized modes (LP modes). However, when the…
Opti2D Graph Control
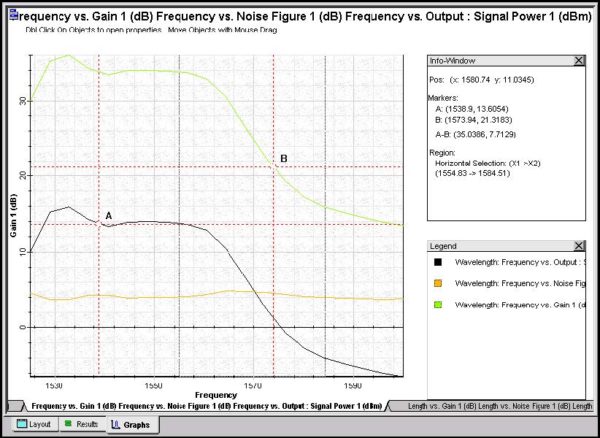
The Graph control is a versatile, powerful easy-to-use tool for observing data (see Figure 4). This section gives a brief description of some of the 2D graph control features and an explanation of how to use them. Figure 4: Opti2D Graph Control User interface features Features Description Large data handling capabilities Opti2D Graph control is…
Script Language for User Defined Functions

The script language OptiGrating 4.2 uses is a programming language based on the BASIC language syntax. You use the script language to define the shape, chirp, and apodization of a grating. To enter this definition, you have to choose the User Defined option. Variables, Arrays, and Operators Variables A variable name can be any string…
View Properties of 2D Graphics
When a View is displayed, it is in the form of a two-dimensional graph, and there are a certain number of properties that can be modified for this graph. Right-clicking anywhere on this Graph View will make a context menu appear with options that can be performed on the Graph View. These options include Zoom…
File
File: Open File: New > Module option > File: Open The Open command OptiGrating allows you to open the following files: .IFO OptiGrating data files (those from IFO_Gratings 1.0, IFO_Gratings 2.0, IFO_Gratings 3.0, and IFO_Gratings 4.0) have an .ifo extension. .IWS All workspace files (see Save Workspace) are saved with this extension. In each Workspace…
Edit
The Edit menu allows you to use one of the following command: Undo Reverses one or more of your last commands. You can use Undo only when you are in Memo mode, i.e. only when you are copying text. (View: New > Memo).
View
The View menu can display and hide elements from the user interface (for example, the Toolbars and the Status Bar). Status Bar When enabled, displays the Status Bar; when disabled, hides the Status Bar. The Status Bar is placed at the bottom part of the user interface. It gives you different prompts and tells you…
Calculation
The Calculation menu allows you to do your calculations quickly and efficiently. Run To perform your Calculation, Spectrum, and Pulse Response calculations, just click either Run from the Calculation menu or the Run button on the Toolbar. In the dialog box that opens, you can see when the calculation is completed. Scan To perform your…
Parameters
The Parameters menu gives you access to all grating parameters: Fiber/Waveguide, Mode, Grating, Dispersion. Fiber/Waveguide Depending on which module you calculate, the Fiber/Waveguide command gives you the basic parameters about fiber or waveguide profile, including refractive index profile, Photosensitivity profile. Mode Shows a list of supported modes for entered Fiber/Waveguide Parameters. Grating Opens the Grating…
Tools
The Tools menu gives you quick and easy access to the following OptiGrating tools: FWHM Tools Automatically calculates the Full Width At Half Maximum (FWHM) of the current. Group Delay Automatically calculates the group delay slope, GDD, and ripple. Phase Selects the Phase Display mode when you are working with Phase graphs. You can toggle…
Settings
The Settings menu gives you a fast and easy access to the General and Display Settings dialog boxes and to the Profile Palette. General Settings File: New > Module option > File: Settings > General Using the General Settings command The General Settings command allows you to define the general settings you will use in…
Window
The Window menu allows you to use the following commands: New Active Window, New Multiple Window, New and Tile, Cascade, Tile, Arrange Icons, and Next. New Active Window Clones the window you are currently working with. New Multiple Window Clones the window and the project you are working with. This command is very useful when…
Help
The Help menu offers a choice of the two options: Help Topics and About OptiGrating. Help Topics Displays the OptiGrating Help topics. About OptiGrating Displays the information about the current version of the program. System Info Displays the information of your computer.

