- This topic has 4 replies, 2 voices, and was last updated 8 years, 9 months ago by .
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.
Optiwave software can be used in different industries and applications, including Fiber Optic Communication, Sensing, Pharma/Bio, Military & Satcom, Test & Measurement, Fundamental Research, Solar Panels, Components / Devices, etc..
OptiOmega is a collection of products specialized for photonic integrated circuit simulation. It automates the design flow for
generating compact models from device level simulations. The software package includes two solvers that can be used via
Python scripting: Vector Finite Difference (VFD) Mode Solver and Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) Electromagnetic Solvers.
Download our 30-day Free Evaluations, lab assignments, and other freeware here.

Optiwave software can be used in different industries and applications, including Fiber Optic Communication, Sensing, Pharma/Bio, Military & Satcom, Test & Measurement, Fundamental Research, Solar Panels, Components / Devices, etc..
OptiOmega is a collection of products specialized for photonic integrated circuit simulation. It automates the design flow for
generating compact models from device level simulations. The software package includes two solvers that can be used via
Python scripting: Vector Finite Difference (VFD) Mode Solver and Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) Electromagnetic Solvers.
Download our 30-day Free Evaluations, lab assignments, and other freeware here.

Hello,
I have interfaced Optisystem with Matlab, I want to know how to calculate the overlap integral using the data of the Inputport structure, inside Matlab component?
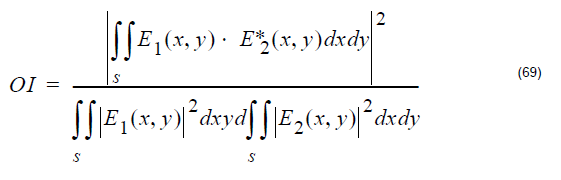
This is basically a numerical integration of the electric field distribution of the input signal. The input signal’s field distribution is found under “InputPort1.Sampled.Spatial.ModeX.Amplitude”. If this is your first time with the Matlab component please go through all of the material on our website like the youtube videos etc. on the subject.
I have already collected the electric field distribution from InputPort1.Sampled.Spatial.ModeX.Amplitude, but I want to know how to calculate the Overlap Integral from the “InputPort1.Sampled.Spatial.ModeX.Amplitude” in Matlab. Is it by using trapz() function in Matlab?
Exactly use trapz function
could you please check the following code:
xc = linspace(0,1,M);
yc = linspace(0,1,M);
A = E1 .* E2;
B = (trapz(xc,trapz(yc, abs(A))) ).^2;
C = trapz(xc,trapz(yc, abs(E1).^2)) * trapz(xc,trapz(yc, abs(E2).^2 ));
OI = B./C;