Gaussian Beam Size
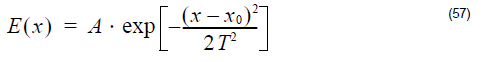
In OptiFDTD, transverse Gaussian Beam is expressed as where x0 is the center position and T is being called as half width. In general, Gaussian Beam radius is the radius at which the field amplitude and intensity drop to 1/e and 1 / e2, respectively. Gaussian Beam Size or Gaussian Beam Spot size is the beam…
2D Total Field / Scattering Field (TF/SF) Region
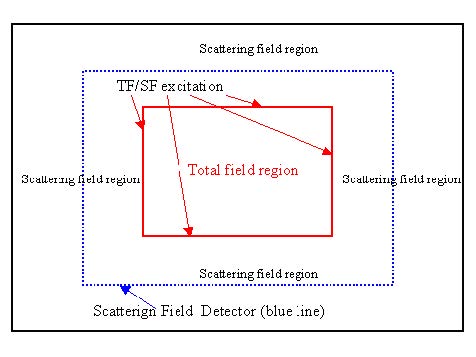
The Total-field/Scattered-field (TF/SF) technique results from attempts to realize any tilting plan-wave source that avoids the difficulties caused by using either the hard source or the boundary conditions. 2D TF/SF is a special type of formula that generates a wave in the enclosed rectangular surface. Inside the rectangular region, it generates the total field (including…
2D FDTD Band Solver Introduction
The band solver in OptiFDTD is an integrated CAD tool and simulation engine for analyzing the photonic crystal and photonic band gap structure. Currently it employs the FDTD method and generates band-diagrams.
Simulation Concept
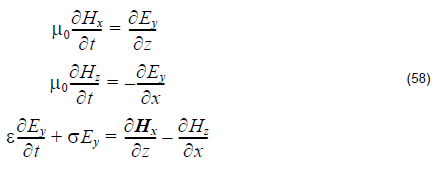
As we know, the periodic structure or the lattice structure has the mode selection function. The task of the band solver is to find these mode positions based on one or several basic lattice cell. The key points for FDTD simulation come from: How can the FDTD method extract the mode? How can the FDTD…
Bloch’s Boundary Condition
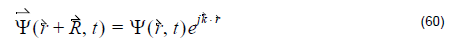
Bloch’s theorem tells us that for periodic structure, field components have the following properties: where R is the lattice vector, k is the wave vector. Equation 60 is the boundary condition used in the OptiFDTD band solver. Initial excitation Unlike conventional FDTD simulations where time domain excitation is continuous wave and lasts on only some time steps,…
Bragg Grating with Layers of Different Width
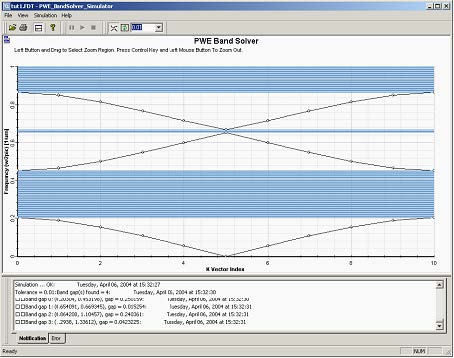
Thanks to the parameterized design we can easily verify other published results as well as point out other features of PWE band solver. Let’s change a variable to 0.2 to simulate grating with alternating layers of different widths. The layer of the high permittivity (waveguides) will be 0.2a thick, whereas the air layer will be…
References
[1] J. B. Pendry, “Calculating photonic band structure”, J. Phys., No. 8, 1085-1108, 1996. [2] A. J. Ward, J.B. Pendry, ” Calculating photonic Green’s functions using a non-orthogonal finite difference time-domain method”, PACS.
Far Field Transform
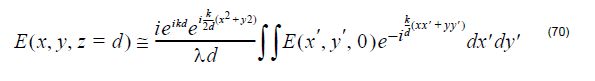
Fraunhofer approximation Narrow angle far-field transform being used in OptiFDTD is based on the Fraunhofer approximation: At a large distance d, the far field position can be expressed by the far field angle, Where the x-directional angle (θx) is the angle between the original yz-plane and the shortest straight line connecting the point and the Y…
RCS Calculation
Consider figure 21, which depicts an observation point in the far field many wavelengths away from the near field path . In this case, the Far Field can be identified as: for TE simulation and for TM simulation. Then the bistatic radar cross section (RCS) in two dimension can be defined as: Figure 23: Geometry…
References
[1] Justin Peatross and Harold Stokes, “Physics of Light and Optics”
Four Wave Mixing Introduction
OptiFDTD provides two dimension nonlinearity and multiple input wave simulations, thereby enabling you to simulate the Four Wave Mixing (FWM) effect. The following lesson outlines how OptiFDTD performs a FWM simulation. To create the Four Wave Mixing layout, perform the following procedures. Designing a four-wave mixing layout To design the four-wave mixing materials, perform the following…
Plane Wave Expansion (PWE) Method Introduction
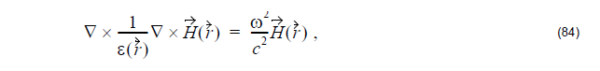
The Maxwell equation in a transparent, time-invariant, source free, and non-magnetic medium can be written in the following form: where ε() is the space dependent dielectric function, c is speed of light in vacuum, and is the optical magnetic field vector of a definite frequency ω with time dependence eiωt . This equation is sometimes called the…
References
[1] J.D. Joannopoulos, R.D. Meade, and J.N. Winn, “Photonic crystals, Molding the flow of light”, Princeton University Press, 1995. [2] S.G. Johnson, J.D. Joannopoulos, “Block-iterative frequency-domain methods for Maxwell’s equations in a planewave basis”, Optics Express 8, no.3, p.173-190, 2000. [3] S.Guo, S.Albin, “Simple plane wave implementation for photonic crystal calculations”, Optics Express 11, no.2, p.167-175, 2003.
Power Transmittance Calculation with VB Scripting Introduction
Access to the simulation results data of Observation objects is a critical feature required for layout sweep simulations and optimization of designed devices. During the simulations, observation objects collect time domain data. The time domain data are stored in the Analyzer file. The OptiFDTD Analyzer provides all tools necessary for post-simulation analysis of the results.…
References
FDTD basic references [1] Yee, K. S., “Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell’s equations in isotropic media,” IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 302-307, (1966). [2] Chu, S. T., Chaudhuri, S.K., “A finite-difference time-domain method for the design and analysis of guided-wave optical structures,” Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2033-2038, (1989). [3] Taflove, A., Hagness,…

